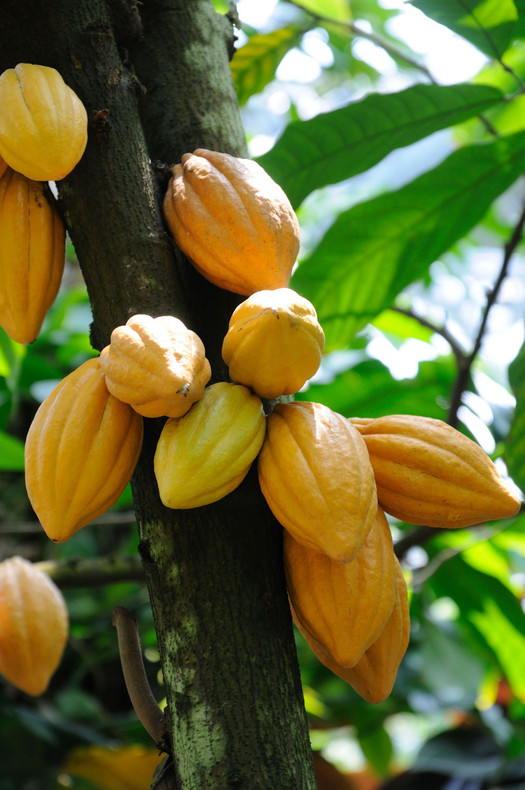
Fact sheet – cocoa and chocolate
Chocolate comes from the fruit of the cocoa tree - not Belgium
The Chocolate Lifecycle
A highly productive Charley’s cocoa tree and the components of chocolate - cocoa pod, wet beans, dried beans and a finished chocolate bar

Where is cocoa grown
- Cocoa grows in areas of high rainfall and temperature which means the wet tropics.
- Major cocoa growing countries are Ivory Coast and Ghana (70% of production) followed by Indonesia, Nigeria, Brazil, Cameroon and Mexico where they have low labour costs; limited capital investment.
- Near neighbour Pacific countries that grow cocoa are PNG, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji where Australia funds development projects.
- Australia and Hawaii have growing cocoa industries. In Australia it’s around Mission Beach and Mossman in far North Queensland. These are high labour, high agricultural values and capital-intensive countries
Where is cocoa traded
Cocoa is a traded commodity. Dry beans in canvass bags find their way from Africa to Europe, the Americas and Asia. There is a global price for West African cocoa – approx US$2,500 per tonne (1,000kgm) of dried beans.
What is in your chocolate bar ? - Check the label
- The FAO (Food and Agricultural Organisation) Standard for chocolate and chocolate products specifies the minimum cocoa percentage of different chocolate types (eg milk, dark). Think 20% plus cocoa as a base.
- What is the other 80%?? Check the label; but it’s often sugar. Sugar is cheaper than cocoa. It might also be palm oil which is cheaper than cocoa butter.
What is in a Charley’s single origin chocolate bar ?
- 70% cocoa nibs and cocoa butter and 30% sugar.
- Charley’s is different to a commercial chocolate bar.

How far has your chocolate travelled – least to most distance travelled
1) Tree to bar - think paddock to plate. The cocoa is grown and the chocolate is made in the country of origin. Charley’s grows its cocoa, makes and sells its chocolate at the plantation, which is rare.
2) Bean to bar - using imported dry beans. In Australia we have Haigh’s, Cadbury as examples and other craft chocolate makers. West Africa, Pacific or South America to Australia.
3) Imported chocolate mass - chocolate blocks are imported from a wholesaler eg Barry Callebaut and then re-melted and converted to chocolate products by the retailer. Boutique chocolate shops often say Belgium Chocolate. But this is probably West African beans, made into chocolate blocks in Europe and then sent world-wide for finishing.
4)Imported finished chocolate product. Think up market European brands. West Africa – Europe - Australia
References
The history of chocolate – see https://www.charleys.com.au/chocolate-story/
Where does my chocolate come from - https://www.charleys.com.au/blog/-where-does-my-chocolate-come-from/
How much sugar is there in chocolate - https://www.charleys.com.au/blog/how-much-sugar-is-there-in-chocolate/